Kubernetes Backup and Restore
Bacula Secures Your Clusters – From GitOps to Tape.
Kubernetes orchestration delivers impressive agility when it comes to deployment as a whole, but its dynamic nature also tends to create complex challenges in the data protection department. Critical application data and configurations must be in a recoverable state at all times in order to maintain service continuity, even when pods fail or clusters experience catastrophic issues. Native Kubernetes tools (etcdctl, kubectl) can only offer basic snapshot capabilities, lacking the scheduling automation, retention management, encryption, and compliance features all enterprise environments need.
Bacula Enterprise is a great example of one such enterprise-grade backup and recovery solution, offering purpose-built Kubernetes backup capabilities through direct API integration to protect clusters, persistent volumes, and application configurations without the prerequisite to install agents or disrupt running workloads. The platform in question takes care of everything from development clusters with only dozens of pods to production infrastructures that handle thousands of containers at once. Bacula’s solution offers automated protection capabilities that capture complete application state regardless of how complex its deployment really is.
Basic cluster snapshots are no longer enough in a modern-day enterprise environment, especially with all the compliance requirements in mind. As such, businesses now need encrypted backups, immutable storage, granular recovery options, and detailed audit trails to prove that their data protection efforts meet all the necessary regulatory standards. Bacula Enterprise offers enterprise-grade data protection capabilities, addressing frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and many other industry-specific regulations while maintaining the high level of speed and flexibility that Kubernetes users expect by default.
Bacula is not just able to back up raw volumes or cluster snapshots, but can also reconstruct entire applications in a usable state, including:
- Persistent data → Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs), storage classes, CSI snapshots.
- Configuration & metadata → ConfigMaps, Secrets, annotations, labels.
- Deployment context → Deployments, StatefulSets, Helm charts, Operators.
- Service exposure → Services, Ingress rules, and networking dependencies.
Bacula Enterprise is also fully compatible with both Tanzu, Rancher Longhorn, OKD and many other Kubernetes-related environments.
Bacula Enterprise’s Kubernetes Backup Features
- Kubernetes cluster resources configuration backup
- Ability to restore single Kubernetes configuration resource
- Able to backup and recovery persistent data
- Ability to restore Kubernetes resource configuration to local directory
- Consistency-ensured backup and restore of persistent volumes
- Ability to restore Kubernetes persistent volumes data to local directory
- CSI Snapshot support
Bacula Enterprise’s Kubernetes module can backup a number of Kubernetes Resources, including, but not exclusive to:
- Deployments
- Pods
- Services
- Persistent Volume Claims
Kubernetes Plugin Configuration & Deployment
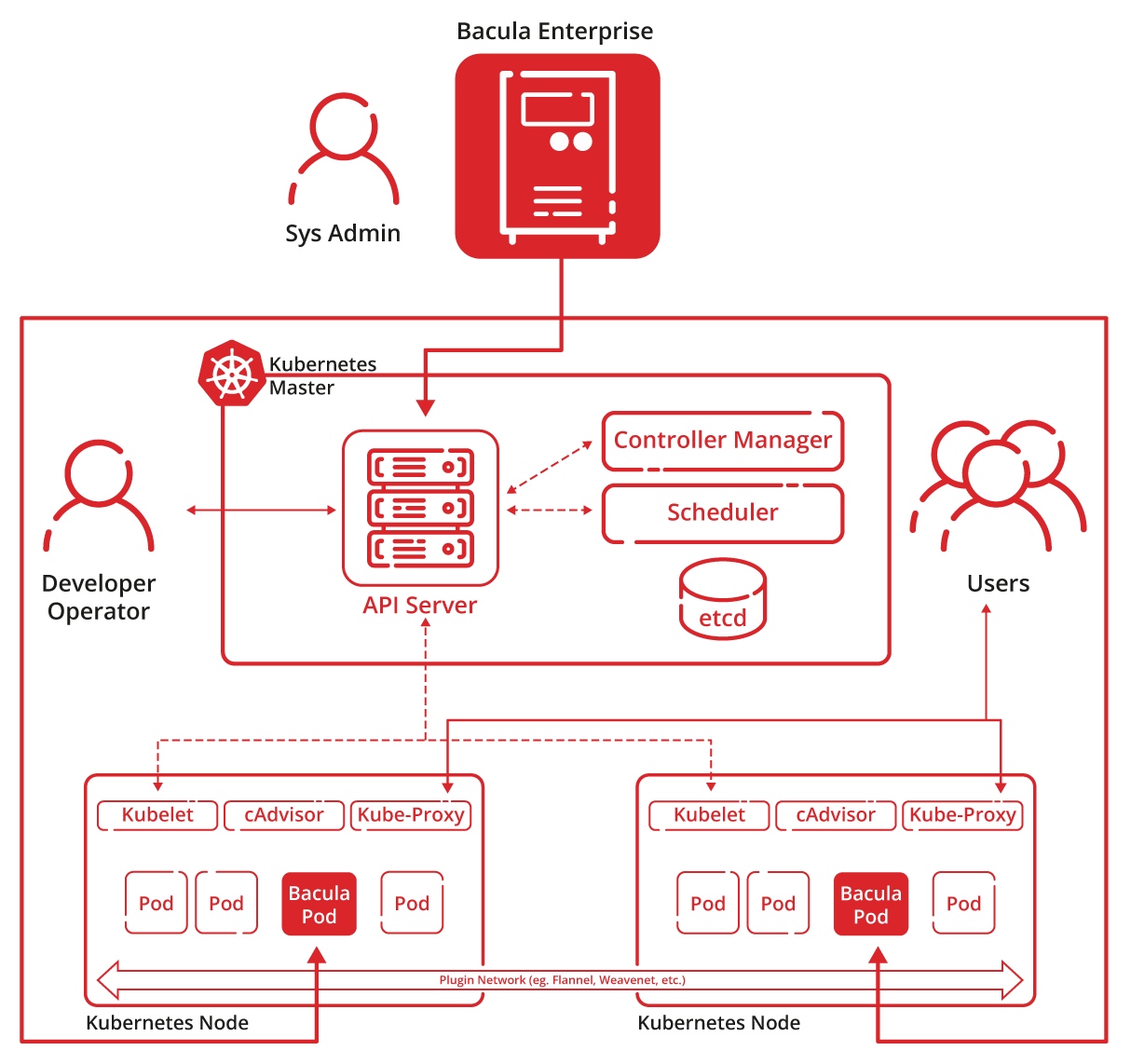
Plugin Architecture and Integration
- File Daemon Module Design – Uses a standard Bacula File Daemon plugin that integrates with existing Bacula infrastructure with ease, preventing the need for separate backup servers or dedicated management layers for Kubernetes environments specifically.
- Flexible Deployment Options – Bacula can be installed onto Kubernetes master nodes, worker nodes, or external management servers with network access to the Kubernetes API, granting extensive flexibility in terms of deployment based on security requirements and network architecture.
- Zero Workload Modification – Capable of securing clusters without changing container images, Kubernetes manifests, or running pod configurations, which removes the necessity to coordinate application teams or plan changes to deployment pipeline.
Cluster Access and Discovery
- Multiple Authentication Methods – The solution can connect to Kubernetes clusters using kubeconfig files, service account tokens, or in-cluster authentication for pods that run within Kubernetes, providing support for diverse security architectures and deployment scenarios.
- Automatic Resource Enumeration – Plugin queries Kubernetes API to discover namespaces, deployments, services, persistent volumes, and other resources that are available for protection, creating opportunities for backup planning and validation before the job is executed.
- Namespace-Level Selection – Aims toward specific namespaces for backup or excludes system namespaces from protection jobs, providing granular control over which cluster components are to receive backup coverage.
Backup Operation Workflow
- API-Driven Data Capture – Retrieves cluster configurations and persistent volume data via Kubernetes API calls, not filesystem access, to ensure compatibility with various storage backends and container runtime environments.
- Backup Proxy Pod Deployment – Launches temporary proxy pods (with low resource consumption) within the cluster automatically in order to facilitate persistent volume data transfer; those pods are also removed automatically after backup completion to avoid additional cluster resource consumption outside backup windows.
- Configurable Execution Control – Both pre-backup and post-backup commands can be executed within specific pods to create application-consistent backups of databases or stateful applications (the ones that require quiescing before data capture).
Restore Operation Controls
- Dual Restore Destinations – Recover Kubernetes resources directly to clusters via API or export configurations and volume data to local directories for all kinds of purposes.
- Flexible Naming Options – Workloads can be restored with either original names for in-place recovery or new, generated, names based on original identifiers and job metadata (for parallel testing environments or blue-green deployment scenarios).
- Selective Resource Recovery – The plugin offers a choice between complete clusters, individual namespaces, specific deployments, or single persistent volumes based on recovery scope requirements to avoid unnecessary restoration of unaffected infrastructure during targeted recovery operations.
Administration and Monitoring
- Unified Management Console – Configure and monitor Kubernetes backup jobs through Bacula’s BWeb graphical interface alongside other infrastructure protection, eliminating need for separate Kubernetes-specific backup administration tools.
- Command-Line Automation – Use bconsole for scriptable job configuration, automated restore testing, and integration with existing operational runbooks and disaster recovery procedures.
- Comprehensive Logging – Captures detailed operation logs including API interactions, resource processing status, and data transfer metrics for troubleshooting, performance analysis, and compliance documentation.
Kubernetes Backup and Restore Module Benefits
Agentless Cluster Protection
- API-Level Integration – Protects Kubernetes clusters through direct API communication without installing backup agents inside container images or modifying pod specifications, eliminating maintenance overhead and security concerns associated with in-container backup software.
- Zero Infrastructure Changes – Backs up running clusters without requiring modifications to Deployments, StatefulSets, or Helm charts, allowing protection of existing workloads immediately without rebuilding images or updating Kubernetes manifests.
- Automatic Workload Discovery – New namespaces and deployments matching backup policies receive protection automatically without manual job configuration, ensuring consistent coverage as Kubernetes infrastructure scales and evolves.
Complete Application State Capture
- Unified Configuration Backup – Captures all Kubernetes resources defining application behavior including Deployments, Services, ConfigMaps, Secrets, Ingress rules, and resource quotas as cohesive backup sets rather than isolated components.
- Persistent Data Protection – Safeguards application state stored in Persistent Volume Claims alongside cluster configurations, ensuring workloads can be restored with their data rather than just empty container definitions.
- Consistent Cluster Snapshots – Coordinates backup of etcd cluster state with persistent volume data to maintain consistency between Kubernetes control plane configuration and actual application storage, preventing recovery of mismatched infrastructure states.
Flexible Recovery Operations
- Granular Restore Capabilities – Recover entire clusters, individual namespaces, specific deployments, or single persistent volumes based on recovery requirements, avoiding unnecessary restoration of unaffected infrastructure during targeted recovery scenarios.
- Cross-Cluster Mobility – Restore Kubernetes workloads to different clusters for disaster recovery, migration between cloud providers, or creation of development environments from production backups without dependency on original cluster availability.
- Configurable Workload Startup – Control whether restored applications start automatically for immediate service recovery or remain stopped for validation and configuration review before bringing workloads online in production environments.
Enterprise Operational Integration
- Centralized Multi-Cluster Management – Protect multiple Kubernetes clusters across different distributions, cloud providers, and on-premises installations from a single Bacula Enterprise deployment, eliminating need for separate backup solutions per environment.
- Unified Infrastructure Protection – Integrate Kubernetes backup with existing Bacula jobs protecting databases, virtual machines, and physical servers, providing consistent backup policies, retention management, and recovery procedures across entire IT infrastructure.
- Policy-Based Automation – Define backup schedules, retention policies, and storage destinations once and apply automatically to Kubernetes clusters matching criteria, reducing administrative overhead while ensuring consistent protection standards.
Safe & Efficient Deployment of Kubernetes Clusters
Effective DevOps environments must be scalable and automated wherever possible. Bacula Enterprise is designed to be stable, reliable and highly scalable and its container backup modules are aimed at easing the workloads of IT and DevOps departments using Docker, Kubernetes, SUSE, or Openshift. It makes Kubernetes significantly safer and more convenient to deploy.
Whether your deployed container environment is used for lift-and-shift of monolithic applications, or refactoring legacy applications, or building new distributed applications – developers and systems administrators can use Bacula’s advanced Kubernetes backup technology with an especially high level of flexibility – via either Bacula’s GUI or command line interface. Remember, this high level of flexibility and customization possibilities are fundamental to Bacula’s approach: to empower the user by introducing a wide range of options to achieve their goals.
Why Backup Kubernetes Environments?
As stateful applications increasingly move to Kubernetes, protecting persistent data and cluster configurations becomes critical for production environments. Organizations must maintain SLAs and ensure containerized services remain available in correct states, making effective backup and recovery essential for any production Kubernetes deployment.
Bacula Enterprise enables cluster mobility through flexible restore operations. Organizations can restore persistent volumes and configurations to different Kubernetes clusters, supporting migration between cloud providers, disaster recovery to alternate sites, and rapid environment replication for testing. This flexibility reduces vendor lock-in and simplifies multi-cloud Kubernetes strategies across AWS, GCP, Azure, and private infrastructure.
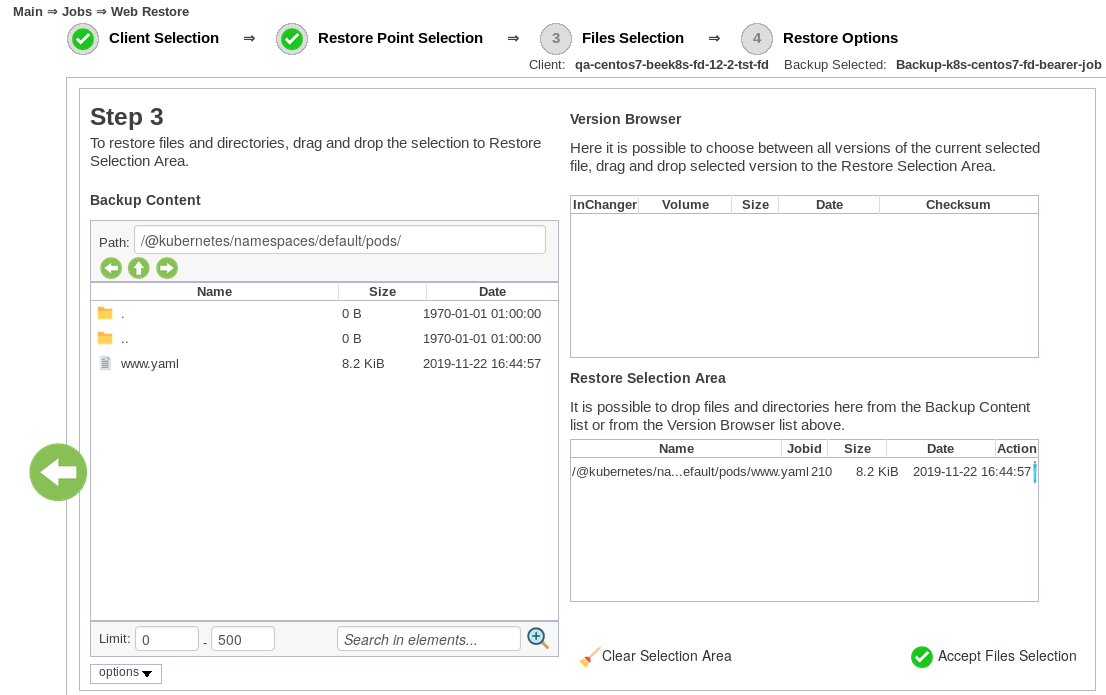
Kubernetes Restore Process
The Bacula Kubernetes backup module provides a choice of two targets for restore operations:
- Restore directly to Kubernetes cluster
- Restore to a local directory
To ensure best practice backup and recovery for Kubernetes container environments, data should be backed up automatically and system administrators should test backups regularly to make certain that they will do what is needed when recovery is necessary.
Core Enterprise Capabilities for Every Bacula User
The Kubernetes backup module operates within Bacula Enterprise’s comprehensive data protection platform. All features described in this section are platform-wide capabilities available across every Bacula deployment, including Kubernetes environments.
Data Protection & Compliance
Enterprise security and regulatory compliance are fundamental to Bacula’s architecture:
- Encryption Throughout the Backup Chain – AES-256 encryption protects Kubernetes configurations, persistent volume data, and etcd backups from capture through network transmission to final storage destinations, with flexible key management supporting both centralized and distributed architectures.
- Ransomware-Resistant Storage – Integration with WORM (Write Once, Read Many) storage systems and immutable backup targets prevents unauthorized modification or deletion of Kubernetes backup data, protecting against ransomware attacks and malicious insider threats that target backup infrastructure.
- Role-Based Permission Systems – Granular access controls restrict which administrators can backup specific namespaces, restore particular workloads, or access cluster configurations, enabling separation of duties and limiting blast radius during security incidents.
- Comprehensive Audit Trails – Every backup operation, restore request, and configuration change is logged with timestamp and user attribution, providing the detailed activity records required for compliance reporting, security analysis, and forensic investigation.
- Industry Regulation Alignment – Built-in capabilities address requirements from GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, PCI DSS, and sector-specific regulations through configurable retention controls, encryption standards, and audit logging that demonstrate data protection compliance.
- Zero-Knowledge Configuration Support – Architecture enables scenarios where backup administrators manage Kubernetes protection operations without accessing sensitive application data, ConfigMaps, or Secrets contained within backups.
Recovery & Business Continuity
Comprehensive restore capabilities ensure rapid recovery from any failure scenario:
- Cross-Distribution Data Movement – Extract and restore Kubernetes resources between different distributions and platforms, enabling migrations from on-premises to cloud, between cloud providers, or from one Kubernetes flavor to another (EKS to AKS, Rancher to OpenShift, etc.).
- Multi-Site Backup Replication – Automatically copy Kubernetes backups to geographically distributed locations, protecting against site-level disasters and ensuring recovery point availability regardless of primary data center status.
- High-Frequency Protection Schedules – Support for backup intervals measured in minutes rather than hours provides near-continuous protection for rapidly changing containerized applications, minimizing potential data loss windows.
Storage Infrastructure & Efficiency
Bacula maximizes storage value through intelligent data management and destination flexibility:
- Global Deduplication – Eliminates duplicate data blocks across all Kubernetes backups regardless of namespace, cluster, or backup job, storing each unique block only once to dramatically reduce storage consumption.
- Configurable Compression Algorithms – Applies compression that balances CPU overhead against space savings based on data characteristics, with algorithm selection optimized for Kubernetes workload patterns.
- Perpetual Incremental Architecture – After initial full backup, all subsequent operations capture only changed data, eliminating recurring full backups and their associated storage and time requirements.
- Sparse Data Handling – Recognizes and processes sparse files and volumes intelligently, backing up only allocated blocks rather than empty space commonly found in persistent volume claims.
- Network-Efficient Operations – Change-tracking algorithms minimize bandwidth utilization by transferring only modified blocks between backup runs, critical for distributed Kubernetes clusters across multiple sites.
- Heterogeneous Storage Targets – Write Kubernetes backups to disk arrays, NAS/SAN storage, cloud object storage (S3, Azure Blob, Google Cloud Storage), tape libraries, or any combination based on retention and performance requirements.
- Automated Tiering Workflows – Migrate backup data between storage classes based on age, access patterns, or custom policies, moving older Kubernetes backups to economical long-term storage automatically.
- Universal S3 Compatibility – Integrates with any S3-compatible storage provider including AWS, MinIO, Wasabi, Backblaze B2, and others for flexible, cost-effective long-term retention.
Enterprise Management & Control
Centralized administration tools provide visibility and control across Kubernetes backup operations:
- Dual Management Interfaces – Choose between graphical web console (BWeb) for visual management and full-featured command-line tools for automation, scripting, and DevOps workflow integration.
- Multi-Tenant Architecture – Service providers and large organizations can create isolated environments with independent Kubernetes backup configurations, separate resource pools, custom branding, and distinct administrative boundaries.
- Detailed Reporting Framework – Generate backup status reports, storage utilization analysis, compliance documentation, SLA metrics, and performance statistics with scheduled delivery to stakeholders.
- External Integration Points – Connect with monitoring platforms, ITSM ticketing systems, SIEM solutions, and identity providers (LDAP, Active Directory) for unified IT operations and single sign-on.
- Automated Resource Discovery – Detects and inventory Kubernetes clusters, namespaces, persistent volumes, and deployments across infrastructure with query capabilities supporting backup planning and verification.
- Workload Impact Controls – Adjust backup concurrency, bandwidth limits, and resource allocation to balance protection speed against production Kubernetes cluster performance impact.
- Unlimited Scale Architecture – Design supports environments from single development clusters to thousands of production Kubernetes installations under centralized management with distributed backup execution.
Economic Advantages
Bacula Enterprise’s licensing model eliminates capacity-based pricing obstacles:
- Cluster-Independent Licensing – Number of Kubernetes clusters, namespaces, pods, or persistent volumes doesn’t affect license costs, enabling unlimited containerized infrastructure expansion without budget constraints.
- Predictable Investment Planning – Straightforward pricing structure eliminates budget surprises as Kubernetes adoption grows, container counts increase, or data volumes expand across the organization.
- Resource-Agnostic Cost Model – Pod counts, StatefulSet quantities, PVC sizes, and etcd backup volumes don’t trigger licensing increases, unlike competitors who price based on protected capacity or resource units.
- High-Volume Economic Benefits – Organizations protecting substantial or rapidly scaling Kubernetes infrastructures gain increasingly significant cost advantages compared to capacity-based licensing competitors.
- Service Provider Profitability – MSPs and hosting providers can offer enterprise Kubernetes backup capabilities while maintaining healthy margins unconstrained by tenant cluster growth or data expansion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why not just use native Kubernetes backup tools?
Native tools like etcdctl provide basic cluster snapshots but lack enterprise features like encryption, compliance reporting, long-term retention policies, and centralized management across heterogeneous infrastructure. They also don’t integrate Kubernetes backups with broader IT backup strategies covering databases, VMs, and physical servers. Bacula Enterprise provides unified protection across your entire infrastructure while meeting regulatory requirements and audit standards.
How does backing up Kubernetes clusters differ from backing up virtual machines?
Kubernetes clusters consist of multiple interconnected components—etcd state, persistent volumes, ConfigMaps, Secrets, and resource definitions—that must be captured as a cohesive unit rather than individual disk images. VM backups capture entire machine states at the hypervisor level, while Kubernetes backups require API-level integration to understand container orchestration and application dependencies. The dynamic, ephemeral nature of pods means backup solutions must track rapidly changing workloads and capture both infrastructure configuration and application data separately.
Can I backup Kubernetes clusters while they’re running?
Yes, Bacula performs backups of running Kubernetes clusters without requiring downtime or pausing workloads. The plugin captures cluster state and persistent volume data through the Kubernetes API while applications continue operating normally. For applications requiring consistency, Bacula can execute pre-backup commands within pods to quiesce databases or flush buffers before capturing data.
How do I restore to a different Kubernetes distribution?
Bacula restores Kubernetes resources as standard YAML configurations and persistent volume data that can be applied to any compliant Kubernetes distribution. During restore, you specify the target cluster connection details, and Bacula recreates namespaces, deployments, services, and data on the destination platform. Some distribution-specific features may require manual adjustment, but core workloads typically transfer between EKS, AKS, GKE, OpenShift, and standard Kubernetes installations.
What happens to my data when pods are deleted?
Pod filesystem data is lost immediately when pods are destroyed unless you’re using persistent volumes to store application state externally. Ephemeral containers running without PVCs lose all data written during their lifetime when terminated. Bacula’s automated cluster backups capture both the pod configurations needed to recreate containers and the persistent volume data containing critical application state, ensuring complete recovery regardless of pod lifecycle events.
Further help on Kubernetes container backup:
- Need to see all our backup solutions? Full hypervisor and database support.
- Our server backup solutions include tools for Windows, Linux and more.
- View Bacula Enterprise data backup and recovery program features.
- Does Bacula support your storage type? Take a look at out storage backup solutions.
- Read our vision on flexible and scalable backup software systems.
- Interested in Sybase backup and recovery? Take a look at our SAP ASE backup solution.